1 中国科学院 重庆绿色智能技术研究院, 重庆 400714
2 中国科学院大学, 重庆 400714
通过化学溶液法一步制备锗/MXene复合材料, 在MXene表面均匀负载了锗金属纳米颗粒。采用SEM和TEM对Ge/MXene复合材料进行了微观形貌分析, 探索了复合材料的形成过程, 结果表明, Ge/MXene复合材料是二维结构形貌, 其元素分布均一。用Ge/MXene复合材料制备了电极, 并组装成纽扣电池进行充放电性能测试, 对电池的比容量、倍率、循环稳定性能进行了系统分析。测试结果表明, Ge含量为50%时的电化学性能最佳, 0.2C下第5~100圈的容量稳定在1200 mAh/g, 载量为1 mg/cm 2; 载量提高到2 mg/cm 2时的比容量依然能达到450 mAh/g。
MXene 锗纳米颗粒 锂离子电池 负极材料 MXene Ge nanoparticles lithium-ion batteries anode materials
1 中国移动通信集团江苏有限公司 规划技术部,南京 210029
2 中国移动通信集团设计院有限公司 有线所,北京 100080
3 烽火通信科技股份有限公司,南京 210019
为满足光传送网(OTN)系统截面容量大幅提升的需求,探索具有代表性的技术演进方向,中国移动在现网环境下基于G.654E新型光纤部署了长距离超100 Gbit/s干线OTN系统,集中应用一批OTN应用领域的前沿新技术,组织测试,得到了新型光纤的承载性能优势、实用传输距离、多种波道类型并存、能效和在线测量功能等实测结果,对关键新技术的应用价值评估和具体引入策略建议可作为下一阶段系统部署的参考。
光传输 干线OTN 部署实践 长距离 超100 Gbit/s optical transmission backbone OTN application G.654E G.654E long-haul beyond 100 Gbit/s
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所 高功率激光单元技术实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
采用高温熔融法制备百分比为(100-x)(23.6Al2O3-53CaO-7.7BaO-2.1Na2O-10.3Ga2O3-3.1B2O-0.2Er2O3)-xYb2O3(x=0,0.9,1.9,2.8,3.6,4.5)的铝酸盐玻璃。应用差示扫描量热法、吸收光谱、荧光光谱、红外光谱以及拉曼光谱等检测手段, 系统研究了不同Yb3+离子引入量对玻璃的物性、热稳定性、Er3+离子光谱性质和结构的影响。结果表明,Yb2O3含量越高, 玻璃的密度和折射率越大, 抗析晶能力有所增强。随着Yb2O3的增加, 玻璃在976 nm吸收系数增大, 对应于Er3+离子的2H11/2→4I15/2、4S3/2→4I15/2以及4F9/2→4I15/2跃迁的527, 549, 666 nm的上转换发光、红光与绿光发光强度比以及对应于4I13/2→4I15/2的1.53 μm近红外荧光强度明显增加。当Yb2O3浓度为3.6%时, 铝酸盐玻璃样品在近红外1.53 μm荧光最强, 此时Yb3+→Er3+正向能量传递效率η1最大, 约为82.9 %。该系列铝酸盐玻璃中Er3+离子1.53 μm最大发射截面为0.77×10-20 cm2, 荧光半高宽最大值为39.4 nm, 荧光寿命最大值为4.46 ms。
铝酸盐玻璃 Yb3+/Er3+共掺杂 上转换发光 1.53 μm发光 aluminate glass Yb3+/Er3+ co-doping up-conversion emission 1.53 μm emission
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Laser Fusion Research Center, Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900, China
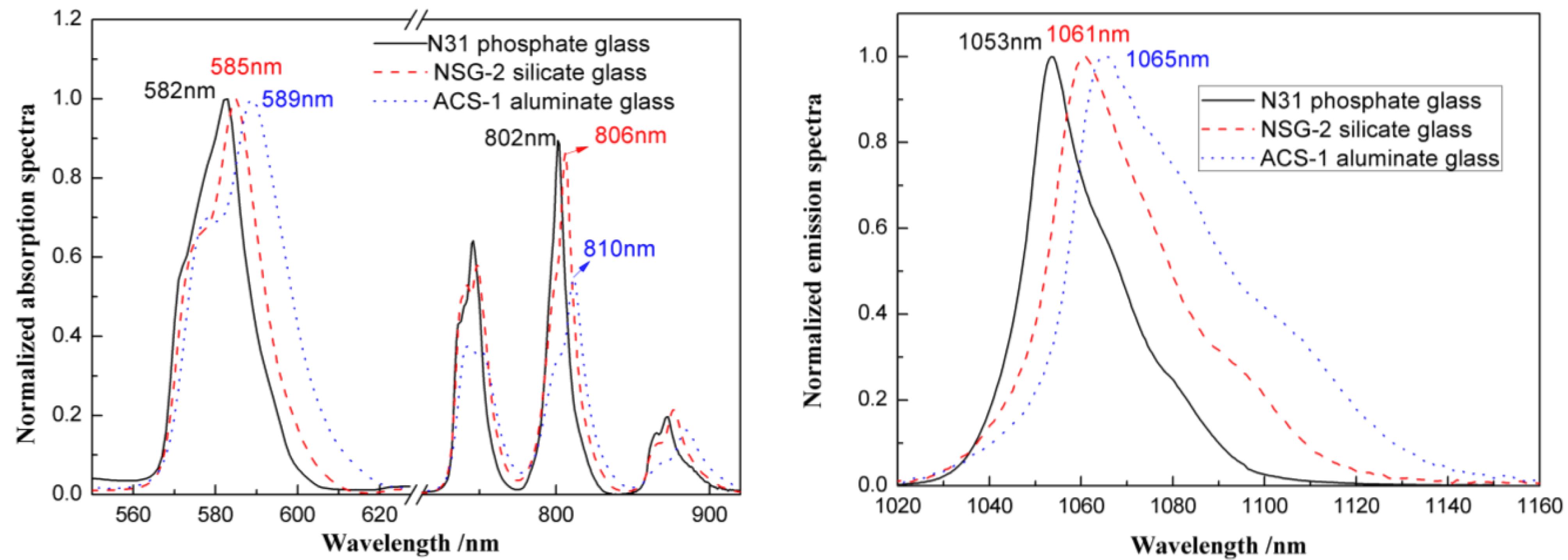
This work presents a brief introduction on three kinds of newly developed $\text{Nd}^{3+}$-doped laser glasses in Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM), China. Two $\text{Nd}^{3+}$-doped phosphate glasses with lower thermal expansion coefficient and thermal shock resistance 4 times higher than that of N31 glass are developed for laser processing. Nd:Silicate and Nd:Aluminate glasses with peak emission wavelength at 1061 and 1065 nm, effective emission bandwidth of 34 and 50 nm, respectively, are developed for Exawatt-class laser system application. Fluorophosphate glasses with low nonlinear refractive index ($n_{2}=0.6{-}0.86$) and long fluorescence lifetime ($430{-}510~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{s}$) are investigated for the purpose of decreasing B integral in high-power laser system. The properties of all these glasses are presented and compared with those of commercial neodymium laser glasses.
aluminate glass fluorophosphate glass high-power laser neodymium laser glass phosphate glass silicate glass High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(1): 010000e1





